CSS Cheatsheet
Ruleset
A ruleset is how CSS applies styles to specific elements. To define a ruleset, use:
- A selector
- Opening curly bracket (
{) - A set of declarations
- Closing curly bracket (
})
Example
p {
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
}
Declaration
A declaration is a specific CSS property set to a property value. To define a declaration, use:
- Property name
- Colon (
:) - Property value
- Semi-colon (
;)
Example
color: red;
Selector
A selector specifies which part of the HTML to style.
Element selector
The element selector selects all elements of the given type. Use the tag type that appears in the HTML.
Examples
p {
/* styles all paragraphs */
}
a {
/* styles all hyperlinks */
}
ID selector
The ID selector selects one specific HTML element based on its id attribute value. Use the hashtag (#) followed by the value of the id attribute for the element.
HTML
<h1 id="header1">Header1</h1>
CSS
#header1 {
/* styles the specific h1 */
}
Class selector
The class selector selects HTML elements based on the value of their class attribute. Use the dot (.) followed by the value of the class attribute.
HTML
<h2 class="dark-mode">Title</h2>
<p class="dark-mode">Subtitle</p>
CSS
.dark-mode {
/* styles the h2 and p and any other element with "dark-mode" as a class */
}
Pseudo-class
A pseudo-class selects an HTML element in a particular state. Use a normal selector, followed by a colon (:) and the name of the pseudo-class.
Example
p:hover {
/* selects all paragraphs when the user hovers over them */
}
Property/Value
A property is an identifier that defines which feature to style. A value describes the specific style for the property. Refer to https://htmldog.com/references/css/properties/ to see a complete list of available properties.
Examples
* {
background-color: black; /* changes the background color */
border: 1px solid red; /* adds a solid red border with 1px width */
box-shadow: -2px 2px 5px black; /* adds a black shadow with 5px blur, 2px to the left and 2px down */
cursor: pointer; /* makes the cursor into a hand */
font-family: cursive; /* sets the font to comic sans */
font-size: 20px; /* sets the size of the text to 20px */
height: 500px; /* sets the height to 500px */
width: 500px; /* sets the width to 500px */
transition: color 1s; /* specifies that when this element changes its color property, it will take one second */
transform: rotate(90deg); /* specifies that this element should rotate 90 degrees */
}
Bootstrap
Bootstrap is a CSS framework designed to make a webpage responsive out-of-the-box. This means it should look good on any device, so the elements automatically morph and shift based upon the viewer window.
Bootstrap link
Include the following link within the <head></head> element to import Bootstrap's CSS:
<link href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
Bootstrap classes
Bootstrap CSS comes with many built-in class rulesets. Add these to elements on an HTML page after importing the Bootstrap stylesheet and the styles will apply automatically.
jumbotron: creates a big banner header from adivtext-center: centers textcontainer: adds space on the sides of adivrow: creates a grid row (usually used on adivwithin a "container")col-md-*: creates a grid column (used ondivs within "row"s)
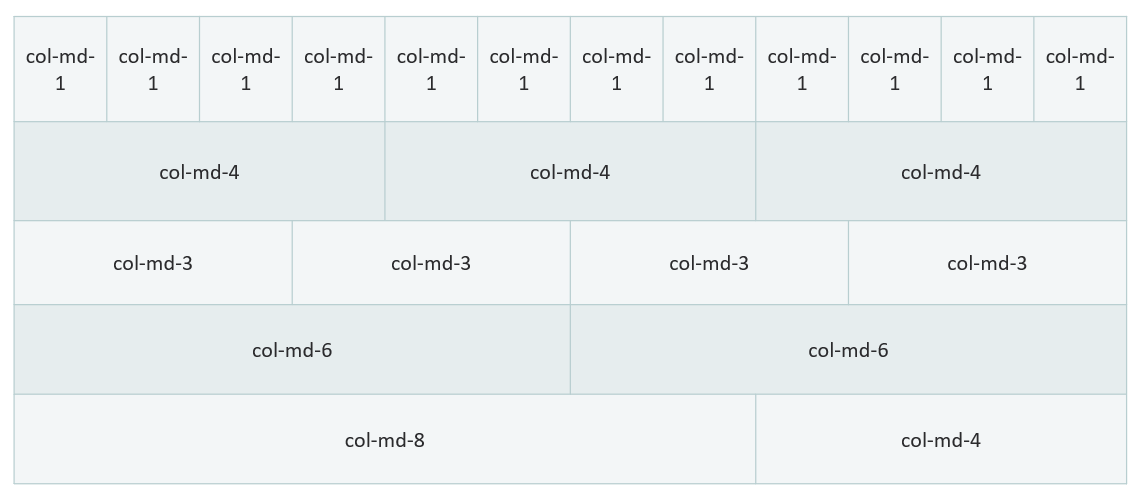
Bootstrap columns
When creating columns within a Bootstrap row, there are 12 total units for width. These 12 units are distributed equally throughout the width of the row. A column can take up any number of these 12 units, but all columns in the row should add up to 12 total units. To set the width on a Bootstrap column within a row, add a class of col-md-*, replacing "*" with the number (1-12) of single columns for the width.